When you search for something on Google, you get several choices as a result. With each click, these results change appearance according to our wishes, and we receive a beautiful, functionally sound feedback. We know these results as websites, and their creation is known as Web development. The term web development sounds familiar because it is one of the most trendy skills you can acquire in the IT field.
Web development is one of the most important parts of IT because it creates a bridge between the user and the provider. Moreover, through functionality, it helps us automate complex tasks. Front-end and Back-end are integral parts of web development. What are these parts? How do they differ from each other? How much does the functioning of a website depend on them? Does one of them stand higher than the other?
If you’re interested in the answers to these questions, you’ve come to the right place, because in this blog you’ll learn about the importance and functions of Front-end and Back-end.
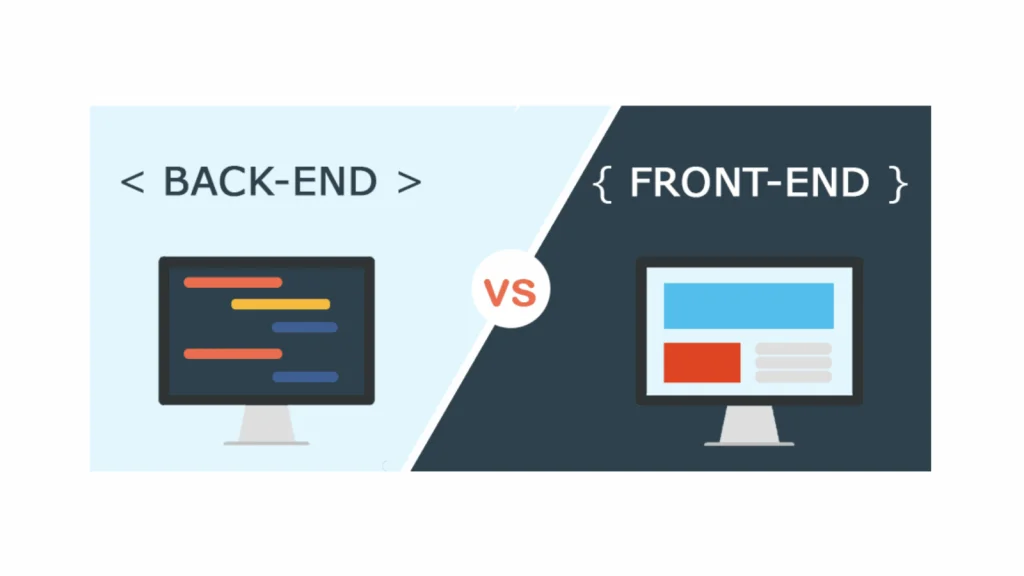
As the name suggests, Front-end is what the user sees, connects with, and experiences. It mainly includes those parts of websites and applications that are visible to the user. The person who works on this is known as a Front-end Developer.
The job of a Front-end developer is to create designs using user interface and experience. The primary skills of a Front-end developer include knowledge of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, as well as frameworks such as Angular JS, Node.js, etc. Along with this, experience in version control systems such as GIT and GITHUB is important. A Front-end developer is an integral part of web development because they ensure the creation of the necessary structure for the work to be performed.
Back-end development resembles the backstage of a movie or show. Actions performed by the user are analyzed and sent back through codes written by the back-end. The person who develops this is known as a Back-end Developer.
The main work of a Back-end Developer involves connecting all aspects to databases and the Front-end. The primary skills of a Back-end Developer include knowledge of languages such as C#, Python, Java, Ruby, etc. Back-end is very important because it gives purpose and functionality to the beauty of an application or website.
Along with a wide range of functions, Front-end has many characteristics:
Client-side rendering: It allows developers to render the entire website on the user’s browser using JavaScript. Server-side rendering: It makes it possible to visualize sites directly in users’ browsers based on changes requested by the users themselves. Optimization: Refined adjustment of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript ensures fast loading of sites for users.
Like Front-end, Back-end is also equipped with many functions that are useful for developers:
Databases: Stores data needed for the user. Website architecture: It involves understanding the goals needed to create an application. Scripting: Involves correct formatting of the construction. API: Application Programming Interface or API are tools that involve communication between technologies and provision of necessary data.
HTML: Hypertext Markup Language or known as HTML, is a markup language used in building web pages. The language contains elements that provide the basic layout of the website. Along with giving structure to websites, it also displays images or visuals. Its advantages are: ease of use, support for multiple browsers, and combination with other languages. Its disadvantages are: static nature, security, and huge pile of codes.
CSS: Cascading Style Sheets or CSS resembles the interior design of a website. CSS is simple because the language more or less includes basic English. Its advantages include multiple browser support, simplicity, and speed. Its disadvantages include cross-browser bugs and it’s also tiring for beginners.
JavaScript: JavaScript is the most important and popular language of Front-end development. It provides flexibility and responsiveness to the website. Advantages include: simple nature, speed, and additional or extended functionality such as creating dialog boxes, forms, pop-up windows, etc. Disadvantages are: difficulty in debugging and browser support. However, JavaScript is also used in the back-end.
Elm: Elm is a simple language used to create fast and continuous websites.
SASS: SASS is another scripting language like CSS. SASS has unique features that give users a seamless experience. Advantages include: reusability and clear codes. Disadvantages include: finding problems and solving them.
jQuery: jQuery is a JavaScript library that enhances HTML event handling and animations. It’s very concise and reduces the number of lines of written code.
Vue.js: This is a framework built around JavaScript and is used to create compact web applications.
AngularJS: It’s a web framework built around JavaScript. It provides features for HTML templates and increases performance.
React: This is a popular JavaScript framework that enhances user interface components and provides a dynamic nature to web applications.
Python: Python is a widely used back-end development language. Its advantages are: huge collection of libraries, easy-to-read codes, integrations, versatility, etc.
PHP: This is another widely used language in back-end development. Its features include: security, platform compatibility, object-oriented programming features, and integration with databases.
Java: This is widely used to create Android and desktop applications. Its features include: automatic memory allocation, portability, and one-time compilation.
Ruby: Ruby is a general-purpose language that has features such as a large standard library, flexibility, scalability, etc.
Django: This is a high-level web framework that has built-in add-ons. It’s best for large-scale, data-oriented, interactive web applications. However, it’s not recommended for small-scale projects.
Flask: Flask is a micro-framework based on the Python language. It doesn’t need libraries or tools and, therefore, is suitable for small projects.
Ruby on Rails: Ruby on Rails is a web application framework written in Ruby. It’s used in developing flawless data table formation and migration. Simple compilation and testing is its additional advantage.
CakePHP: CakePHP is a popular web framework for PHP. It’s used in developing both small and large applications because it’s easier to configure and provides complete security.
Difference between Front-end and Back-end Development Front-end is the interactive part of a website or application. The graphical user interface (GUI) allows users to perform actions according to their wishes. Users can see and connect with the Front-end. Users cannot see the backstage of the website or application, i.e., the Back-end. It collects information from users, processes it, and ensures the functioning of the application.
A Front-end developer works on layout, while a back-end developer’s job is to achieve the functional stage.
Front-end developers should have an idea about Back-end. Thus, its development is not just about beauty. Although back-end development mainly concerns logic, calculations, servers, APIs, and testing, collaboration and data exchange between front and back developers is very important.
So, as you can see, web development is an interesting field in the technology sector. Front-end Development resembles the exterior of a house; paint, wall carvings, wall hangers, or everything a person can see and feel. Back-end resembles the electrical supply, building materials that you can’t see, but are crucial for the house. These two things together give an application the best appearance and functionality.

შეავსე ქვიზი და მიიღე პერსონალიზებული რეკომენდაციები კარიერულ გზასთან დაკავშირებით
დაწყება
ყოველგნარი გაუგებრობის თავიდან აცილების მიზნით, გთხოვთ, ყურადღებით გაეცნოთ ამ წესებს და პირობებს კურსის შეძენამდე.
1. რეგისტრაცია
2. განმარტებები
3. კურსზე რეგისტრაცია
4. დასწრება და მონაწილეობა
5. ანგარიშსწორება
6. ინტელექტუალური საკუთრების უფლებები
7. პასუხისმგებლობის შეზღუდვა
8. გაუქმების პოლიტიკა
9. სერტიფიცირება
10. ცვლილებები
11. კონფიდენციალურობის პოლიტიკა
12. დამატებითი პირობები
13. პირობების მიღება
14. მოქმედი კანონმდებლობა
To avoid any misunderstandings, please carefully review these terms and conditions before purchasing the course
1. Registration
2. Definitions
3. Course Registration
4. Attendance and Participation
5. Payment
6. Intellectual Property Rights
7. Limitation of Liability
8. Cancellation Policy
9. Certification
10. Changes
11. Privacy Policy
12. Additional Terms
13. Acceptance of Terms
14. Governing Law and Jurisdiction





